수험생에게 어려운 Deferred Tax 파헤치기 (부제. Permanent Difference와 Temporary Difference 차이점)
수험생에게 어려운 Deferred Tax 파헤치기
(부제. Permanent Difference와 Temporary Difference 차이점)
# 회계처리 하는데 왜 세금당국의 또 다른 기준이? Why, 회계기준 VS IRS?
Corporation은 매년 회계말이 지나면 IRS가 만든 Rule에 따라 IRS에 세금보고(Income Tax Filing)를 해야한다. 사실 회사는 별도로 회계처리를 하지만 과세 당국은 당국의 과세법에 의해 제대로 돈이 걷혀지고 있는지 관심이 있지 회계처리를 잘하고 있는지는 사실 관심 밖의 사항이다. 다만, 당국은 세금 Filing이 잘되고 있는지를 효율적으로 확인하기 위해 회사의 회계문서를 참고자료로서 활용하는 것이다.
그렇다면 회계처리와 세금보고가 전혀 공통점이 없느냐? 그것은 아니다. 비슷하긴 하다. 하지만 목적이 다르기 때문에 차이가 나는 것이다. 회계는 발생주의(Accrual Basis)에 따라 수익과 비용을 근거로 당기순이익을 정확히 산출하여 정보이용자에 정확한 수익 및 재무상태표를 주기 위함이고, 세금보고는 현금주의(Cash Basis)에 의거 익금과 손금이라고 하여 (말은 다르지만 수익 비용 대응한 컨셉으로 이해하면 됨) 정확한 과세표준을 계산하고 있는지를 확인하는 것이다. 그래서 회계의 수익과 세금 익금을 계산하는 기준이 대동소이 다르고, 비용과 손금의 기준이 다르다. 그래서 회사는 이러한 Difference 값들을 추적하여 운영하여야 하고 청산하는 그날까지 그 차이가 나지 않음을 증명해야 하는 의무가 있는 것이다. (이 파트는 먼 훗날 AICPA 따고 한국 세무사가 되는 그날에 제대로 업뎃해 보겠습니다..미션2)
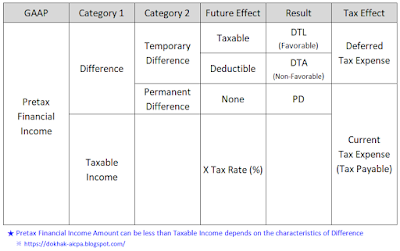
위의 그림은 일단 GAAP과 Tax와의 컨셉이 '다르다'는 것을 직관적으로 이해하기 쉽게 적어 놓은 것이니 자세한 건 디테일하게 공부해야 합니다. 같은 비즈니스 활동을 두고도 해석이 다르다는 사실!(왜냐 해석하는 법(法)이 다르기 때문이다)
참고. 기본적인 용어 차이를 짚고 넘어가자. 부르는 것도 달라서 시작부터 헛갈리게 한다.
ⓐ GAAP → Income Tax Expense
현행 GAAP으로 산출한 발생주의 기준 수익에 Tax Rate(세율)을 적용한 금액으로써 Current Tax Expense와 Deferred Tax Expense로 이루어짐
ⓑ IRS → Income Tax Payable
현금주의와 발생주의 차이를 모른다면 이 블로그의 게시 글 'Cash Method vs Accrual Basis Difference 현금주의와 발생주의의 차이' Click!하여 읽고 먼저 이해하고 올 것!
# 단계별로 Deferred Tax의 큰 그림을 이해하자!
1. 문제에서 Pretax Financial Income 파악하기
2. 주어진 조건 중 Pretax Financial Income에 가감요소 확인
+ Excess of taxable revenue over book revenue
- Excess of book revenue over taxable revenue
- Excess of deductible amount over book expense
+ Excess of book expense over deductible amount
---------------------------------------------------------
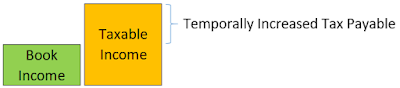
Taxable Income
3. 위에서 구한 Taxable Income에 당기 법인세율을 곱하여 당기 Tax Payable을 구함
4. Pretax Financial Income에 Tax Expense을 빼주어 Net Income을 구함
※ Tax Expense(Current와 Deferred) 둘다 빼야 함
6. 유효법인세율(Effective Tax Rate)을 구함
Tax rate: 30%
ⓐ Tax-exempt revenue 10,000
ⓑ nondeductible expense 5,000
※ ⓐ, ⓑ are included in 100,000
> Taxable Income
= 95,000
> Current Tax Expense (Tax Payable)
> Net Income
= 71,500
# Permanent difference, Temporary difference 정의
1. Permanent Difference
Source. https://www.accountingtools.com/articles/what-is-a-permanent-difference-in-tax-accounting.html
크게 PD를 일으키는 두 가지 원인이 있는데, 하나는 정부 지원 활동과 관련되어 세금 보조 혜택을 주는 Tax Exempt (비과세) 항목, 다른 하나는 범칙금과 같이 괘씸죄나 Entertainment 비용 같은 사업과 무관한 비용을 줄이기 위한 징벌적 과세가 있다. 참고로 세금 기조를 보면 정부에서 장려하는 활동인지, 억제하는 활동인지 알 수 있다.
2. Temporary difference
ⓐ A taxable temporary difference is a temporary difference that will yield taxable amounts in the future when determining taxable profit or loss.
In both cases, the differences are settled when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled.
Source. https://www.accountingtools.com/articles/2017/5/15/temporary-difference
1. Permanent Difference 자세히 알아보기
▷ Permanent Difference 적용 수익/비용
- Favorable (Deductible) → Taxable Income에서 빠지는 금액
※ 계산시 Book Income에서 빼줘야 함 → Taxable Income 감소 →Tax 감소
ㆍDomestic production activities deduction 9%
ㆍOther penalties which are deductible
ㆍLife insurance proceeds received by an enterprise on one of its officers
ㆍDividend received deduction
ㆍFederal income tax
※ 계산시 Book Income에서 더해줘야 함 → Taxable Income 증가 → Tax 증가
ㆍ50% nondeductible meals
ㆍPolitical contributions
ㆍFines and penalties paid for government nondeductible
2. Temporary Difference 자세히 알아보기
A temporary difference can be either of the following:
ⓐ A deductible temporary difference is a temporary difference that will yield amounts that can be deducted in the future when determining taxable profit or loss.
ⓑ A taxable temporary difference is a temporary difference that will yield taxable amounts in the future when determining taxable profit or loss.
"Temporary Difference를 한국 세법상 「유보」라 부른다. 자산의 증가(DTA)→유보, 부채의 증가(DTL)→△유보라 구분하는데, 막연하게 들으면 자산의 증가(DTA)가 좋을 것 같은데... 그럴까? 아니다! 현금 흐름 측면에서는 미래 Deductible 되는 세금을 미리 내는 것이므로 unfavorable하다. 왜냐? 지금은 현금은 미래의 동일 현금의 가치보다 높으니까!"
▷ Temporary Difference 적용 수익/비용
※ Tax expense per books is based on book income adjusted for all permanent book/tax differences
ㆍLong Term construction
ㆍUnrealized gain on investment
ㆍGood will
# 분개
① Tax Payable > Tax Expense
② Tax Payable < Tax Expense
# 시험에 외우면 좋은 것들
ㆍRevenue인데 순서상 Financial Income 인식 이후에 Taxable 된다 → DTL
# 연습문제
ⓐ Compute ABC’s book and tax income
ⓑ Compute ABC’s tax expense per books and tax payable
ⓒ Determine the change in ABC’s deferred tax accounts for the year
1번 문제 답을 확인하시려면 아래에서 확인해 주시면 됩니다. (↓)
• Book income = $97,000
($100,000 operating income + $2,000 interest - $5,000 depreciation)
• Taxable income = $80,000
($100,000 operating income - $20,000 deduction)
• Tax expense per books = $33,250
(35% × $95,000 (book income - $2,000 favorable permanent difference for tax-exempt interest)
• Tax payable = $28,000 (35% × taxable income)
→ $5,250 excess of tax expense over tax payable
[Journal Entry Ver1]
Tax expense 33,250
Cash (tax payable) 28,000
Current Tax expense 28,000
Cash (tax payable) 28,000
Deferred Tax Liability 5,250
2. 위 조건과 아래 8가지 조건을 감안하여
ㆍTax rate : Current 30%, Future 40%
① Fines 5,000
② Installment Sales Revenue > Cash received: 53,000
③ Interest on state bond: 2,000
④ Losses accrued according to GAAP for litigation: 30,000
⑤ Premium paid for life insurance to key employees: 10,000
⑥ Depreciation for Book: 20,000 / for Tax 30,000
⑦ Excess of accrued warranty expense: 7,000
⑧ Bad debt expense: 4,000
⑨ Prepaid rental of the Office: 8,000
⑫ Unrealized Gain on holding T/S: 2,000
2번 문제 답을 확인하시려면 아래에서 확인해 주시면 됩니다. (↓)
TD: Temporary Difference

댓글
댓글 쓰기